Mobile is a challenging marketing channel to master. On average, only 4% of your mobile users will continue to use your app after one year. It’s unique – always at consumer’s arm’s reach, but delicate in that it is very personal and does not tolerate spam.
For this reason, the world of mobile marketing is moving towards more relevant, contextual targeting. Location and time are among the most important elements when it comes to mobile and its context. Mobile is (as its name indicates) always on the move and therefore an inherently location-based channel.
As a result, technologies that tap into location-based marketing, such as geofencing and beacons, are getting more and more popular with businesses.
What Is Geofencing?
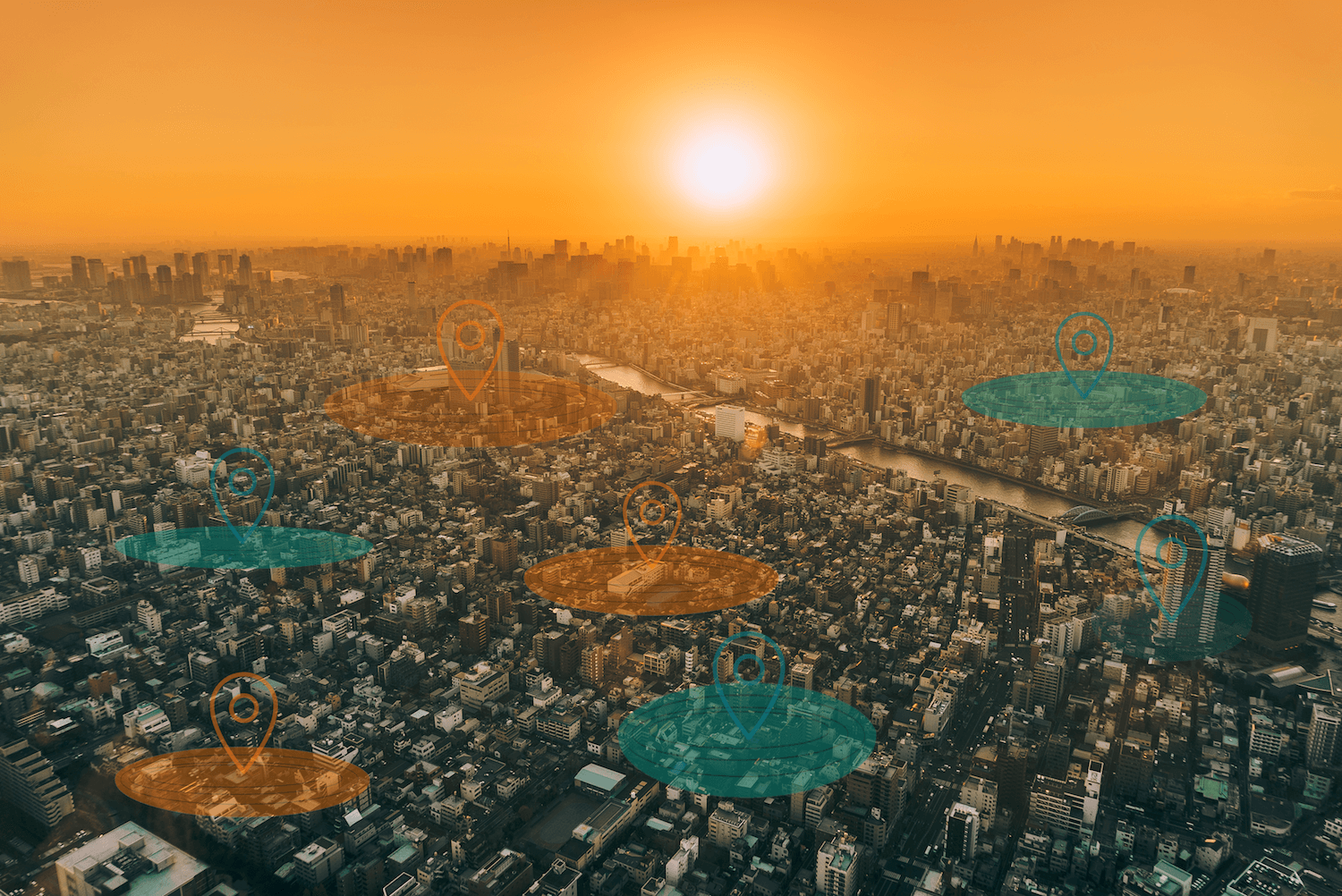
Geofencing is a technology that enables mobile apps to take advantage of location-based marketing. This technology can help marketers collect information and engage app users as they enter, leave or stay in certain geographical areas, also known as geofences.
A geofence is a virtual fence around a real-world location, like a restaurant or an airport. Geofences can vary in scale and shape – they can be as small as a store or as big as a city; they can be round for more straightforward use cases or polygon-shaped for more complex situations.
What Can Marketers Do With Geofencing?
There are a lot of different ways a marketer can use geofencing. To simplify, we’ll say that the majority of geofencing use cases boil down to either interacting with app users within a defined area or learning about their offline behaviors from location data.
Here are a few examples of how marketers can get the greatest ROI from geofencing tactics:
- Increase foot traffic by sending promotional offers to shoppers as they pass by stores
- Suggest products based on previous in-app behaviors
- Improve customer service by capturing feedback, or opening lines of communication between app users and business management
- Integrate social sharing to boost brand awareness
- Geo-conquest competitors by building fences around rival locations and push incentivized content to redirect shoppers
How Does Geofencing Work?
Locations services: To locate a user’s device within a geofence, geofencing uses cellular triangulation, WiFi tower triangulation or GPS. Cellular and WiFi are advised for their reliability as GPS-based solutions have proven to be extremely battery-draining.
Recommended Reading: Location-Based Technology For Mobile Apps: Beacons vs. GPS vs. WiFi
Format: Geofencing doesn’t require hardware. It comes in the form of a software that can be integrated into a mobile app and managed through an online dashboard or API.
Target Range: Geofencing is more beneficial for large-range outdoor targeting. This usually translates to an area between 50 and 50,000 meters in radius, for example, a shopping mall or a neighborhood.
Privacy: A mobile app using geofencing requires user permission to monitor location and send notifications. If you want to learn more about how to target successfully, check out this guide on How to Ask for Location Permissions in iOS11: Recommended Approaches & 10 Examples.
How Does Geofencing Compare With Beacons and Geotargeting?
Geofencing, geotargeting and beacons are all used for location-based marketing. They mainly differ in the way they generate location data and establish a target range. To decide which one is more suitable for your app, you can use the comparison table below.
| Geotargeting | Beacons | Geofencing | |
| Data collection | IP-address | Bluetooth | Cellular/Wifi/GPS |
| Target Range | Large
(state, zip code) |
Small
(store aisle, bus stop) |
Medium to large (store, neighborhood) |
| Real-time targeting | No | Yes | Yes |
| Best for | Browser marketing | Mobile & app marketing | Mobile & app marketing |
| Location data collection | No | Yes | Yes |
| Hardware and maintenance | No | Yes | No |
Critical Considerations For Implementing Geofencing
- It shouldn’t be dependent on GPS – GPS will drain your app users’ battery in no time.
- Geofencing software should be optimized for accuracy and battery usage – Choose a system that has a well-optimized balance between the two, not ones that claim to be super duper accurate; you can bet you’ll find battery draining on the flip side.
- Collect Data – When it comes to interpreting data, you can’t neglect offline behavior. Use these insights to target users in a more personalized way, and go beyond the average push notification.
- Manage your geofencing efforts – A good geofencing solution should come equipped with a management dashboard and API, which allows for easy creation and optimization of geofences.
- Don’t spam your users – Dense urban areas have a lot of geofences. To avoid sending too many notifications it’s critical to research and employ anti-spam tools.
Want to know more? Check out 7 features to look for when choosing a geofencing partner.
How Can You Get Started With Geofencing?
If you’re interested in employing geofencing technology and want to hit the ground running, here are 5 very practical steps to help you get started:
- Make sure geofencing meets the requirements of your existing app strategy
- Choose an appropriate geofencing software to reach your goals (use tips above for guidance)
- Test the software (many come with a testing app)
- Implement the software into your app (you may need app development help with this)
- Get creative with your geofencing notification campaigns (for inspiration, check here)
Closing Thoughts
Geofencing is a profitable tool for connecting with consumers. By developing an app with geofencing technology, you give your business a competitive edge. If done properly, this marketing tactic can build loyalty, generate real-time engagement, and maximize path-to-purchase conversions.