Organizations, of all kinds, from emerging startups to long-established enterprises all contend with the proliferation of mobile app development. Customer expectations are shifting. The mobile user demands convenience and they want instant access to information. At the same time, users want the ability to explore options, regardless of where or when. More importantly, customers expect their experience with companies to be extremely relevant to them. If your organization doesn’t have a mobile strategy, it’s missing out on countless opportunities to connect, engage, influence, transact, and support current and future customers.
But, what are the factors that underlie and influence mobile app success? The answer is complex and evasive for many companies, considering about 40 percent of new products are estimated to fail at launch. The focus of this article is to outline four tactical and organizational success drivers for releasing a new mobile product to market.
Support from Top-Level Management
Support from top-level management is fundamental to mobile app success. After all, senior managers make the final decisions about budget, resources, and project priorities.
It’s senior management’s responsibility to make a long-term commitment to product innovation through research-driven iteration from proving technical feasibility to testing with prototypes and growing in accordance with user feedback. Senior management occupies an involved role in the mobile development process, particularly with resource commitments. Top management needs to guarantee resources for development and secure them so they aren’t redirected towards more immediate needs in times of scarcity. Too many development projects fail from lack of time and financial assurance.
How to Win Support from Top-Level Management
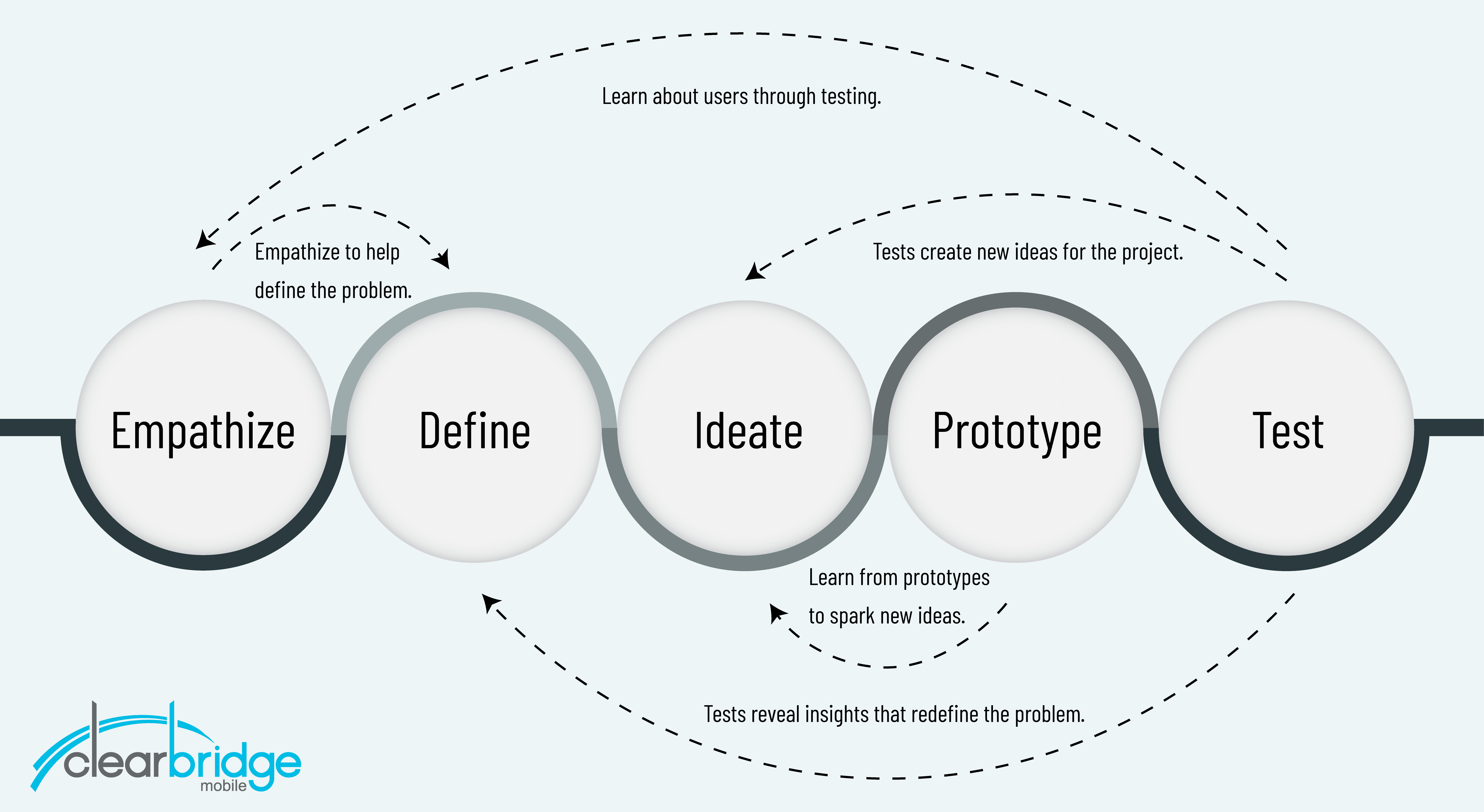
A mobile product needs to go beyond the theoretical to achieve buy-in from senior stakeholders. Top-level management is more likely to take a mobile concept seriously if it’s already been validated and tested on actual users. Mobile app prototyping helps reduce uncertainties and provides a demonstration of how the final product will work.
Prototyping validates an early concept and uncovers opportunities to explore new ideas before the project reaches development. A significant advantage of prototypes is that they create an emotional connection. Stakeholders are more willing to give the go-ahead for a project when they have a connection with the concept. People’s attitudes and perspectives change when they can physically take the product in their hands, use and understand the concept.
Knowledge Transfer and Management
Agile development relies on effective communication, so the mismanagement of knowledge is a significant barrier to implementation. In fact, 75 percent of damage from failed mobile projects is attributable to knowledge silos. Employing cross-functional development teams is essential to eliminating silos and reducing risk in agile environments.
Practicing squad-based development helps improve communication between team members. Squads are small flexible teams who are responsible for the end-to-end delivery of each product. A considerable advantage of squad-based development is all team members have full knowledge of every aspect of the project. Squads make knowledge transfer easy and allow the entire team to retain knowledge for future iterations of the product. Collectively, a team has more knowledge, experience, and insight than an individual. This approach to agile development dramatically reduces knowledge risk to help keep project velocity consistent and predictable.
Follow an Agile Development Process
Proper planning and agile development are essential to combating scope creep, containing development costs and ensuring you achieve your anticipated return on investment (ROI). Throughout the development process, are three essential areas to manage from early conceptualization to product launch. Managing these three areas increase the chances of mobile app success:
- Pre-development work or the design thinking process
- Explicit requirements definition
- Iterative development, specifically following the build-test-learn formula
Mobile product owners who diligently oversee these three phases of development are in the best position to fulfill user needs and maintain satisfaction over time. Also, this approach to product management helps retain development costs while delivering on the overall business purpose of the application.
Pre-Development Work: Using Design Thinking for Mobile App Success
Perhaps the most difficult challenge in planning for mobile app success is getting started. The dimensions of the concept will change several times in the planning process, and that’s to be expected. As your product vision takes shape, the initial blending of ideas is exciting, but to reduce product deviations, product requirements need to be fully defined using an iterative design thinking process.
A thorough grasp of user needs and the competitive landscape is essential to mobile app success. Design thinking supports innovation by observing and considering multiple solutions to a single problem. The core principle of design thinking asserts that a user-centric approach to product development encourages innovation, which leads to market differentiation and competitive advantage.
Another integral part of mobile app success is conducting user experience research. User input needs to be considered throughout the entire lifecycle of the project. Often, market and user research are done too late – specifically as an afterthought once the product design is complete. However, before any development begins it’s important to understand how the user experience (UX) and user interface (UI) will work together to solve user pain points. Design thinking is a formalized framework for processing user data and creating appropriate design solutions to address real user needs. At a high level, the design thinking process identifies the purpose of the mobile product, business objectives, user needs, and mobile app success criteria. A design thinking consultation will prioritize product features and create the user journeys necessary to create a prototype, which is validated (or invalidated) through testing.
Explicit Requirements Definition
A product requirements document forces you to put all of the project’s technical requirements on paper including any necessary and available technologies; required maintenance and support; backend systems integration; scalability and future-proofing; third-party software dependencies; and other considerations.
Two of the biggest risks to mobile app success are scope creep and unclear or changing requirements specification. A product requirements document will create a clear focus for the project. The objective of a mobile app PRD is to fully define the purpose of the project by detailing the business strategy and technical requirements, identifying risk areas and challenging product assumptions.
A PRD addresses both the business strategy and technical feasibility of the project. The document forces you to put all of the project’s technical requirements on paper including any necessary and available technologies; required maintenance and support; backend systems integration; scalability and future-proofing; third-party software dependencies; and other considerations. There is a long list of technical specifications that require devoted attention. A PRD helps you assess the chances of overall success for each individual requirement and within the overall constraints of the project.
How well product requirements are defined before development begins is a major mobile app success factor, impacting both profitability and time-to-market. Essentially, a PRD document functions as a communication tool for all areas of the product and defines explicit objectives for the project.
Iterative Development: Build, Test, Learn, Repeat
Iterative development is the way agile teams handle and process changing information throughout the product lifecycle. An iterative approach to development encourages experimentation, promoting project teams to fail often and fail fast with few cost repercussions. Product iterations, or sprints, limit both market and technical uncertainties by exploring technical solutions with experimentation. The end result is delivering a minimum viable product (MVP).
MVP development follows a build-measure-learn process, which allows you to release a product that can be continually improved as you validate assumptions and learn what users want from the product. An MVP will also set the stage for future iterations of development and clarify the sequential steps to take in the project – whether that’s changing directions entirely or continuing with the set product roadmap.
Market Orientation
Many organizations will focus on delivering a mobile app that functions properly but will leave market research as an afterthought. If you want to achieve mobile app success, you need to begin strategizing before development begins. Every decision made during product development needs to revolve around your users’ needs and motivations. A market focus needs to be present throughout the entire project lifecycle, specifically during idea generation and strategic design process.
Mobile app success is firmly rooted in market research. Not only is market research essential for developing an app that addresses a specific user need, but it’s also a requisite for creating the messaging that will attract users to the product. Every aspect of the product’s branding from its app store listing and website messaging, to its social media presence, content marketing initiatives, press kit collateral, and visual representation must align with its target users.
Final Word
Typically, a person decides whether or not to download an app in only a few seconds, which is why it’s so important to clearly identify your mobile app success criteria. These initial few seconds don’t allow much slack to tell an app’s story or express its unique value proposition and for that reason, mobile app success factors should be thoroughly researched long before the product’s release date. Process and knowledge management implications are clear. Overall, the quality of pre-development planning, market research, and agile process execution make a significant impact on long-term mobile app success.